- Form 16 - Meaning & How to Download Form 16 Online?
- Form 26QB: TDS on Purchase of Immovable Property
- Form 26AS - How to View and Download Form 26AS from TRACES?
- Form 15G & Form 15H to Save TDS on Interest Income - How to Filll Form 15G for PF Withdrawal
- Form 10-IE: Understanding its Significance under IT Act
- Form 27Q - TDS Return for NRI Payments
- Form 16B – TDS Certificate for Sale of Property - Download From 16B from TRACES Website
- What is Form 16A? - How to Get and Fill Form 16A?
- Simplifying Form 13 of Income Tax for Non-Deduction/Lower Deduction of TDS
- Form 16 Password - What is the Password for TDS Form 16 and How to Open Form 16 Password?
- Form 24Q: TDS Return on Salary Payment
Form 16 Explained: Meaning, Uses & How to Download It Online
Form 16 is a certificate issued under section 203 of the Income Tax Act, 1961, by the employer and submitted to the ITD. It contains the details of the tax deducted by the employer, or you can call it proof of all the TDS deducted and submitted to the income tax department. Form 16 serves as a vital document for salaried individuals when filing their income tax returns. It's proof that your taxes have been properly paid to the government.
This guide will help you understand what Form 16 means, Form 16 format, etc.
Income Tax Return filing for FY 2024-25 has begun!
File your ITR on time with expert help – Accurate, timely, and refund-ready! File Today
Latest Update:
This year, the format of Form 16 has been revised to enhance clarity and provide more detailed information.
Earlier, Form 16 included only basic details related to salary and TDS, but the new format offers a comprehensive breakdown of components such as tax-exempt allowances, deductions under various sections (like 80C, 80D, etc.), and the calculation of taxable salary. This revamped structure aims to simplify the Income Tax Return (ITR) filing process, making it more transparent and user-friendly for salaried taxpayers. Upload Form 16 and File your ITR.
What is Form 16?
Form 16 is a certificate issued to salaried employees by their employer that provides a detailed summary of TDS deducted and deposited to the Income tax authorities. Form 16 is an important document issued under the Income Tax Act of 1961 provisions.
Form 16 serves as a TDS certificate displaying the salary earned and TDS deducted from it. The employer issues this certificate by June 15th of each assessment year, following the conclusion of the financial year in which the income was received. If any employer delays or fails to issue Form 16 by the specified date, he is liable to pay a penalty of Rs.100 per day until the default continues. If you changed jobs during the year, you must collect Form 16 from each employer you worked for.
Employers are required to issue Form 16 to their salaried employees on or before the 15th of June of the assessment year for which the income tax return is being filed. For example, for the FY 2024-25 (AY 2025-26) Form 16 should be issued by 15th June 2025.
Types of Form 16
There are two types of Form 16: Form 16A and Form 16B. Both are related to Tax Deducted at Source (TDS), but they serve different purposes. Here is what each form is used for:
Form 16A: Form 16A is a certificate for Tax Deducted at source (TDS) and is provided along with Form 16. Both Form 16 & 16A are TDS certificates, but Form 16 is for individuals who receive income from salary. On the other hand, Form 16A is for all incomes other than salary.
Form 16B: Form 16B is a certificate of tax deducted on the purchase of property; TDS under section 194IA is required to be deducted when a person sells an immovable non-agricultural property for consideration greater than 50 lakhs of rupees. In such a case, the buyer will be required to deduct the TDS of the seller and file form 26QB; after filing 26QB, form 16B will be generated, which serves the basic purpose of the TDS certificate depicting the basic details of the buyer and seller of property and consideration and amount of TDS deduction.
You can read more about From 16A and Form 16B here.
What are the Components of Form 16?
Once you download Form 16, you can check the Form 16 consists of two parts - Part A and Part B.
Part A:
Part A covers quarterly TDS details, along with the employer’s PAN and TAN information. Employers can download this from the TRACES portal. This section contains details such as the employer's and employee's PAN (Permanent Account Number), employer's TAN (Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number), summary of tax deducted and deposited by the employer (TDS), and other relevant details.
Part A consists of the following -
- Name and Address of the employer
- PAN and TAN of the employer
- Employee’s PAN
- Quarterly summary of total salary payments for the relevant FY.
- Summary of quarterly tax deducted and deposited as certified by the employer.
Part B:
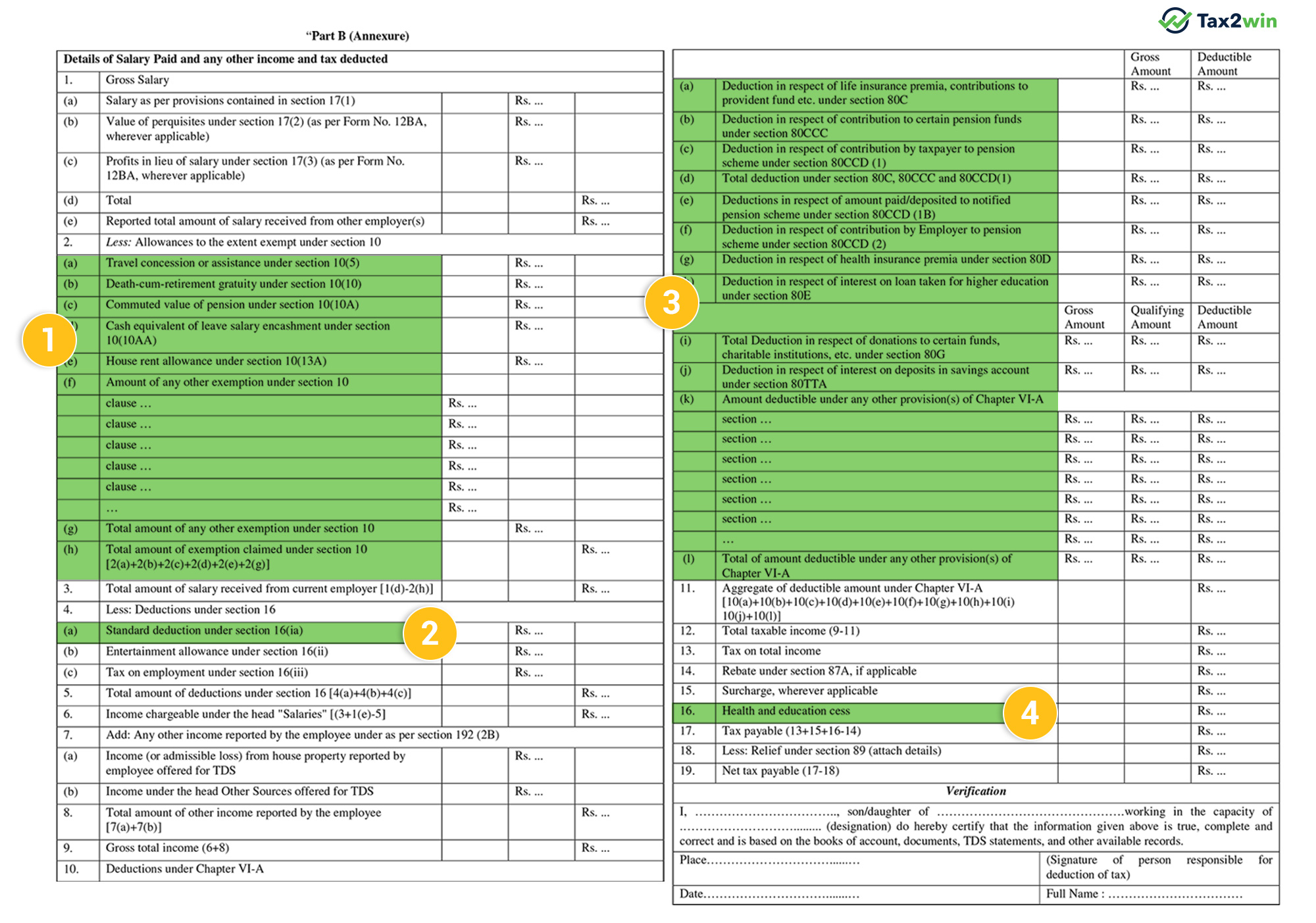
Part B is an annexure to Part A, prepared by the employer, detailing the salary structure and deductions under Chapter VI-A. Part B provides a more detailed picture of your income like the employee's salary, allowances, deductions claimed by the employee (such as under Section 80C, 80D, etc.), and the resultant taxable income. It is an annexure to part A. It also includes details of income from other sources, if any.
Some constituents of Part B are -
- Detailed breakup of salary
- Detailed breakup of allowances exempted under section 10
- TDS deducted by the employer
-
Deductions allowed under the IT Act under Chapter VI-A. Given below is the list of deductions -
- Deduction for Life Insurance Premium paid, contribution to PPF under section 80C.
- Contribution to pension funds under section 80CCC.
- Employee’s contribution to the pension scheme under section 80CCD(1).
- Taxpayer’s self-contribution to a notified pension fund under 80CCD(1B).
- Employer’s contribution to the pension scheme under section 80CCD(2).
- Health insurance premiums under section 80E.
- Donations made under section 80G
- Interest paid on a loan taken for higher education under section 80E.
- Donations made under section 80G.
- Interest income on savings account under section 80TTA.
- Tax calculated, surcharge, education, and health cess charged, relief under section 89.
How Form 16 Helps in Filing ITR
Form 16 serves as a vital document for salaried individuals when filing their income tax returns. It provides key information about the employee's salary, TDS, and deductions. It shows the breakup of salary income and the TDS amount deducted by the employer. The details from Form 16 need to be accurately filled in the relevant sections of the income tax return form. There are certain details that need to be derived from Form 16 while filing ITR. Here is the information required -
- Exempted allowances under section 10
- Break down of deductions under section 16
- Taxable salary
- Income from house property reported by an employee and offered for TDS
- Income under ‘Other sources’ offered for TDS
- Section 80C deductions in detail
- Aggregate of section 80C deductions
- Tax payable or refund due.
Note: Form 16 serves as proof that your employer has deducted and deposited tax on your behalf to the government. This can be helpful in case of any inquiries from the income tax department.
Verification of Form 16
It is essential for employees to cross-verify the details mentioned in Form 16 with their salary slips, bank statements, and Form 26AS (consolidated statement of taxes deducted and paid) to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies. If any discrepancies are found, they should be promptly brought to the employer's attention for rectification.
Why is Form 16 Important for Salaried Employees?
Form 16 acts as proof of tax payment and helps employees reconcile their income and tax deducted. It provides a clear overview of the salary structure and facilitates easy calculation of taxable income. It also helps employees determine their tax liabilities and claim eligible deductions while filing their income tax returns.
When Will Form 16 Be Available For FY 2024-25?
The due date to issue Form 16 for FY 2024-25 is 15th June 2025, and if the employer has deducted TDS on the employee's salary from April '24 to March '25, then Form 16 must be issued by the employer on or before 15th June '25. If the employee loses their Form 16, they can request a duplicate copy from their employer. The employee can also download Form 26AS from the income tax e-filing portal, which contains details of the TDS deducted and deposited against their PAN. This can also serve as proof of the TDS deducted and deposited.
What’s Changed in Form 16 for ITR Filing 2025?
The ITD will soon be releasing the forms for ITR filing FY 2024-25 (AY 2025-26).Taxpayers are advised to stay alert to avoid any last-minute rush. Earlier, Form 16 only had basic details. But now, it will show much more as to which salary components are tax-exempt, how much tax-free allowance you have got and which benefits have been taxed and which salary benefits came under the tax net. This will help reduce confusion during ITR filing, making the entire process clearer and more transparent.
Apart from this, you will also have to provide information whether you have spent more than ₹ 2 lakh on foreign travel or more than ₹ 1 lakh on electricity. This additional information is being sought with the aim of increasing transparency.
Why is Form 16 required?
Form 16 is a crucial document for salaried individuals in India, as it serves multiple purposes:
- Proof of Income and Tax Paid: Form 16 is a certificate provided by an employer to an employee, showing the salary paid during the financial year and the tax deducted at source (TDS) on that salary. It is proof that the employer has deducted and paid the tax on behalf of the employee.
- Income Tax Return (ITR) Filing: Form 16 simplifies the process of filing an income tax return. It provides a summary of the employee's earnings and the tax deducted, making it easier to calculate taxable income and claim deductions.
- Documentation for Financial Purposes: It can be used as proof of income when applying for loans, credit cards, or other financial services.
- Verification by Tax Authorities: If the income tax department has any queries or discrepancies in the income tax return, Form 16 serves as an official document that provides the necessary details of salary and TDS.
- Compliance with Tax Laws: It helps employees and employers ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations, as the form reflects accurate and timely payment of taxes.
Upload Form 16, and our software will automatically pick up all the relevant information from your Form 16 and prepare your tax return. There is no need to enter anything manually. File your ITR hassle-free.
What is the Eligibility of Form 16?
According to regulations released by the Indian government's Finance Ministry, every salaried employee whose tax has been deducted, whether they fall under the tax exemption limit or not, is eligible for Form 16.
If an employee's income does not fall within the taxable band, Tax Deducted at Source is not required to deduct. As a result, in certain situations, the employer is not required to give Form 16 to the employee. However, many organizations now provide this certificate to employees as a good work practice because it contains a consolidated picture of the individual's earnings and has other applications.
Note: If you switched jobs during the financial year, you should receive a separate Form 16 from each employer who deducted TDS from your salary.
Form 16 Format for FY 2024-25
Form 16 Part A
This part of income tax form 16 covers employer, employee, and TDS payment details. It shows quarter-wise details of your tax deposited with the government. Some details are:
- Name and Address of the employer.
- PAN and TAN of the employer.
- Name and Address of the employee
- PAN of the employee
- Summary of taxes deducted and deposited quarterly by the employer



Form 16 Part B
This part shows the detailed computation of Income, based on which tax is being calculated and deducted by your employer. It contains the breakup of the salary earned by you, various deductions, exemptions (if any), and the tax computation after considering all the items based on applicable tax slab rates. The details mentioned in Part B are as follows:
- Whether opting for Taxation under section 115 BAC: Yes or No
(for a better understanding of 115 BAC, please refer to our guide on 115 BAC or click here)
A. Gross Salary(Column 1): This part of Form 16 requires details of salary as per provisions of section 17(1), perquisites, and any profits received in lieu of salary u/s 17(2) &17(3), respectively.
B. Exemptions and allowances considered(Column 2): Earlier in this part of the form, combined information of all the exemptions under Section 10 was provided, but with the introduction of new Form 16, a list of allowances is provided, and the details are required to be filled. The list of allowances is as follows:
- Travel concession or assistance under section 10(5)
- Death-cum-retirement gratuity under section 10(10)
- Commuted value of pension under section 10(10A)
- Cash equivalent of leave salary encashment under section 10(10AA)
- House rent allowance under section 10(13A)
- Amount of any other exemption under section 10
C. Total Amount of Salary received from Current Employer (Column 3): This part of the form calculates the total salary received, including allowances and other perquisites.
D. Deductions under Section 16 (Column 4): All the deduction columns are mentioned below:
- Standard deduction under Section 16(ia)
- Entertainment allowance under Section 16(ii)
- Tax on employment under 16(iii)
E. Total amount of deduction under section 16 (5)
F. Income Chargeable under the head Income from Salaries (Column 6): This column shows the net income from salary after deduction of all the allowances and deductions.
G. Any other income declared by the employee as per section 192(2B) (Column 7): This column of the form enables the employee to declare any other income with the proof of the income like Income (or admissible loss) from the house property, Income under the head Other Sources offered for TDS.
H. Total amount of other income reported by the employee (Column 8): This column provides a total of all income earned by an employee other than salary.
I. Gross Total Income (Column 9): This form column indicates the total income of employees reduced by the exemptions but before deduction under Chapter VI-A.
J. Deduction under Chapter VI-A (Column 10): Earlier, there was no separate list of deductions; an option was to disclose the section under which the deduction has been claimed. But in Form 16, disclosure of deductions is required as per a separate list.
K. Aggregate deductible amount under Chapter VI-A (Column 11): This column totals the deduction amount from all the sections under Chapter VI- A as claimed by the employee.
L. Total Taxable Income (Column 12): This column refers to the employee's net income after considering deductions under Chapter VI-A.This is the amount on which tax is calculated.
M. Tax on Total Income (Column 13): This column specifies the Tax amount as per the applicable tax slabs on taxable income as per column 12.
N. Rebate under section 87A, if applicable (Column 14): This Column specifies the tax rebate, If the total income of a person doesn’t exceed Rs. 5,00,000/- then a tax rebate of 100% of the tax amount will be available to the person under this column subject to a maximum amount of Rs. 25,000 (under old regime) and Rs.60,000 (under new regime), applicable for FY 2025-26 ITR filing.
As per Finance Act 2023, under the new regime, if total income doesn’t exceed Rs. 7,00,000, then a tax rebate of 100% of the tax amount will be available.O. Surcharge, wherever applicable (Column 15): This column refers to the additional tax as a surcharge applicable if income exceeds a certain prescribed limit (currently 50 lac,1cr, 2cr, and 5cr).
P. Health and Education Cess (Column 16): This column is introduced in the new Form 16.
Q. Tax payable (Column 17): This column is calculated as 13+15+16-14.
R. Relief under section 89 (Column 18): This column refers to any relief allowed against the arrear of salary received in the previous year.
S. Net tax payable (Column 19)
How to Download Form 16 from Traces?
Here are the steps that you need to follow to download Form 16 pdf for 2024-25 from the TRACES website -
- Step 1: Visit the official TRACES website.
- Step 2: If you are a registered user, enter your PAN and password to log in to the portal. Otherwise, you can create a new account.
- Step 3: Go to the ‘Downloads’ tab and click on ‘Form 16.’
- Step 4: Select the type fo Form and the financial year for which Form 16 is required.
- Step 5: Verify the PAN number and other details.
- Step 6: Enter the TDS receipt number and select the date of the TDS.
- Step 7: Total the tax deducted and collected.
- Step 8: Click submit to complete the Form 16 download process.
Download Form 16 Part B
- Log on to the TRACES (TDS Reconciliation Analysis and Correction Enabling System) website. The URL for TRACES is https://www.tdscpc.gov.in.
- If you are accessing the website for the first time, you must register an account. Provide all the required details for registration.
- The details you submit during registration will be validated, and your account will be created. Your PAN number will be used as your username, and you can choose a password of your choice.
- An activation link will be sent to your registered email address. You will also receive an activation code on your registered mobile number. Use these to activate your account.
- Once your account is activated, log in to TRACES using your PAN and password.
- In the download section of TRACES, locate and select "Form 16B for Buyer."
- Provide the assessment year, PAN number, and seller acknowledgment number. This information is required to generate Form 16B.
- After submitting the necessary details, Form 16B will be made available for download in the Downloads section of TRACES.
- Download Form 16B and print it out.
- Sign the printed form and deliver it to the buyer.
- The buyer can also refer to their Form 26AS, which is a consolidated statement of total TDS deducted. It includes details reflected in Form 16, Form 16A, and Form 16B, providing a comprehensive overview of TDS deductions.
Downloaded Form 16? Time to file your ITR. Simply upload the downloaded Form 16 here and file your ITR hassle-free.
How do I get Form 16?
Your employer issues form 16; you can expect it by the end of 15th June. But if it’s not issued by the end of 15th June, you may demand it from your employer. Generally, the accounts or HR department issues Form 16. Even if you have left your job, if you have requested, the employer cannot deny providing you with Form 16.
In case any person doesn’t receive his Form 16 and has his TDS deducted, then he/she may intimate the same to the Jurisdictional A.O., who may take appropriate action for the same and, if it finds the employer is guilty, then carry out further proceedings including levy of penalty.
How to file ITR without Form 16?
If you do not have Form 16, you can still file your income tax return by following these steps:
- Gather salary slips: Collect all your salary slips or payslips for the financial year for which you are filing the income tax return. These payslips should contain salary details, allowances, deductions, and any other income components.
- Calculate taxable income: Consolidate the information from your salary slips and calculate your taxable income. Consider all the components of your salary, such as basic salary, allowances, perquisites, bonuses, etc. Subtract any applicable deductions such as house rent allowance (HRA), standard deduction, professional tax, etc. This will give you your taxable income.
- Refer to bank statements: Review your bank statements to identify income sources other than your salary. This could include interest income, dividends, or any other form of income. Include these amounts in your taxable income calculation.
Verify Form 26AS: Access your Form 26AS through the Income Tax Department website. Form 26AS is a consolidated statement of all the taxes deducted and deposited against your PAN. Verify that the TDS details mentioned in Form 26AS match your calculated income details. If there are any discrepancies, contact the deductor (employer or bank) to rectify them.

Read More here.
If you are facing any difficulties with filing ITR or have confusion on multiple Form 16 or no Form 16, you can get assistance from our online CAs.
Resolving Form 16 & Form 26AS Mismatch Issues
If you identify a mismatch between Form 16 and Form 26AS, it is important to rectify the discrepancy. Here are the steps you can take to rectify the mismatch:
- Contact your employer: Inform your employer about the mismatch and provide them with the necessary details and documentation. Share copies of Form 16 and Form 26AS, highlighting the specific areas of discrepancy. Ask your employer to rectify the information in Form 16 and issue a revised form with the correct details.
- Coordinate with your employer: Work closely with your employer to ensure that they promptly rectify the errors in Form 16. Provide any additional supporting documents or information required by your employer to rectify the mismatch.
- Update Form 26AS: After your employer has rectified the errors and issued a corrected Form 16, the revised information should be updated in Form 26AS. However, it may take some time for the updated information to reflect in Form 26AS, as it depends on the timelines of TDS return filing by your employer.
- Cross-verify and reconcile: Once the revised Form 16 and updated Form 26AS are available, cross-verify the information in both documents to ensure that the discrepancies have been resolved. Make sure that the details in Form 16 now match the updated information in Form 26AS.
- File your income tax return: Once you have verified that the mismatch has been rectified, you can proceed to file your income tax return. Use the corrected Form 16 and updated Form 26AS to accurately report your income and taxes while filing your return.
Tips:
- Maintain copies of all communication with your employer regarding the Form 16 mismatch.
- It's recommended to download a fresh copy of Form 26AS before filing your Income Tax Return (ITR) to ensure the latest information is reflected.
Difference Between Form 16, Form 16A and Form 16B
Form 16, Form 16A, and Form 16B are certificates issued for Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) in India, but they serve different purposes and apply to different types of transactions. Here's a breakdown of each:
| Form | Purpose | Applicable On | Issued By | Key Components |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Form 16 | TDS certificate for salary income | Salary paid by employer | Employer | Part A: PAN, TAN, TDS detailsPart B: Salary breakup, deductions, tax payable |
| Form 16A | TDS certificate for non-salary income | Interest, commission, rent, professional fees | Banks, companies, etc. | PAN/TAN of deductor & deductee, payment details, TDS deducted and deposited |
| Form 16B | TDS certificate for sale of property | Sale of immovable property (Section 194IA) | Property buyer | PAN of buyer & seller, property details, sale amount, TDS deducted and deposited |
Points to be Noted while Checking Form 16
PAN and Personal Details
- Ensure that your PAN, name, and other personal details are correctly mentioned.
- Any mismatch can lead to issues in claiming TDS credit.
Employer Details
- Verify the employer’s name, TAN, PAN, and address.
- These should match the employer records and TDS returns filed.
Previous Employer Details
- If you have changed the jobs during the financial year, verify the accuracy of both of the employers.
TDS Deducted and Deposited
- Cross-check the TDS amount deducted and whether it has been deposited with the government.
- You can verify this in Form 26AS or the new AIS (Annual Information Statement).
Salary Breakdown (Part B)
- Check if the salary components like Basic, HRA, Special Allowance, etc., are properly detailed.
- Ensure that exemptions like HRA, LTA, and standard deduction are correctly applied.
Deductions Under Chapter VI-A
- Confirm that deductions under sections like 80C, 80D, 80G, etc., are correctly claimed as per your investment proofs.
Tax Computation and Net Tax Payable
- Verify the total tax liability and whether any tax is payable or refundable.
- Check for any discrepancies in the final tax computation.
Assessment Year
- Ensure that the assessment year mentioned is correct (e.g., FY 2024–25 corresponds to AY 2025–26).
Digital Signature
- Make sure the Form 16 is digitally signed by the employer to ensure authenticity.
Consistency with Payslips/Form 26AS
- Match the figures with your monthly payslips and Form 26AS to detect any mismatches or missing entries.
Form 16: A Vital Document Beyond Taxes
Form 16 is commonly associated with income tax filing, but its utility extends far beyond just taxes. As a comprehensive certificate of your income and TDS (Tax Deducted at Source), Form 16 plays a critical role in various financial and administrative processes. Here are four essential tasks where Form 16 proves to be extremely useful:
Visa Application Process
Planning an international trip? Most embassies require proof of financial stability before granting a visa. In such cases, Form 16 serves as a credible document that demonstrates both your income and tax compliance. When submitted along with your salary slips or bank statements, it enhances your chances of visa approval by establishing your financial reliability.
Applying for a Loan
Be it a home loan, personal loan, or car loan, lenders need evidence of your income and repayment capability. Form 16 provides a detailed summary of your total earnings and tax deductions for the financial year, helping banks or NBFCs assess your creditworthiness. If you’re missing payslips or bank statements, Form 16 can act as a strong alternative for income proof during the loan application process.
Credit Card Applications
When applying for a credit card, financial institutions evaluate your income to determine your eligibility and credit limit. For salaried individuals, Form 16 offers a quick overview of annual income, even in the absence of regular salary slips or other documents. This makes it easier to meet the criteria for credit card approval.
Switching Jobs
Transitioning to a new job? Employers typically request proof of previous income for tax calculations and structuring your salary package. Form 16 provides a consolidated summary of your earnings and taxes paid, which simplifies documentation during job change—especially if you no longer have access to earlier pay slips.
Got your Form 16? File ITR with Tax2win
- Upload Form 16: Simply click on the link https://tax2win.in/efile-income-tax-return/upload-form16 and upload your Form 16.
- Review: Our advanced AI-integrated software automatically picks up the required information & fills in your details by itself. Simply review the information.
- File ITR: As soon as you give your confirmation, our system files your income tax return online.
The ITR filing for FY 2024-25 is about to begin, and so is the rush to file ITR. Pre-book your filing now and avoid the last-minute rush. Book an online CA now!
FAQ’s on Form 16
Q- How to rectify errors in Form 16?
If there is any error in Form 16 because of the employer’s mistake, then the same can be rectified by your employer at your request. Subsequently, a revised Form 16 will be issued to you by your employer. Provide them with the necessary details and documentation to support your claim. They will rectify the errors and issue a corrected Form 16.
Q- I haven’t received any Form 16 from my employer; do I still need to file my income tax return?
If your Gross Total Income exceeds 2,50,000, filing an income tax return is mandatory. Your employer can issue form 16 only when he has deducted tax from your salary. If your employer does not deduct tax and your income exceeds the specified limit, then even if you don’t have Form 16, you are required to file your income tax returns.
There are various other conditions also, other than income above 2,50,000, due to which a person would be mandatorily required to file ITR, Major those are
- Deposit of more than 100 lac in one or more current accounts during the year.
- Incurred expenditure of more than two lacs on foreign travel.
- Incurred expenditure of more than 1 lac on electricity
Q- I haven’t received Form 16; how do I calculate my Salary Income?
If you haven’t received Form 16, you will have to refer to your salary payslips, bank statements, tax-saving investment proofs, home loan certificates, education loan certificates, Form 26AS, etc., for filing income tax returns. While payslips contain details of your income, like basic salary and allowances, Form 26AS contains the details of all your taxes deducted and taxes paid.
The Form 26 AS can be viewed/downloaded from the Income Tax Department’s online portal, i.e., https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal
Q- My employer has deducted tax from my salary, but neither he issued me a Form 16 nor my Form 26AS shows any such deduction entries.
In such a case, it may be possible that your employer has deducted the tax from your salary but has not deposited it the same to the credit of the Government account. You have to pay the full amount of tax while filing your income tax return. Also, you should immediately bring this matter to your employer's notice or default.
Further, the employee should intimate the same to the Jurisdictional A.O., who may take appropriate action for the same, and if the employer is found guilty, then carry out other further proceedings, including a levy of penalty.
(As per Gujrat high court decision on 30/11/2021 in the case of Kartik Vijaysinh Sonavane v. DCIT - [2021], it was held that TDS benefit would be given to the employee even in case TDS has not been deposited by the employer)
Need a CA to bail you out of this situation? Connect Now.
Q- I switched my job during the year; how should I file my ITR now?
In case you had two employers for the particular financial year, you will get Form 16 from both employers for the respective months you served. The income tax return will be filed by combining the details of both Form 16s. But you must be careful in doing so because it might happen that your former and present employer has calculated your tax after taking into consideration the basic exemption limit. In such a case, you are not entitled to take advantage of the exemption limit twice.
The same applies to all deductions and allowances during the year, as any deduction/allowance can be claimed only once or as per the respective rules of the income tax law, even if it is reflected in both Form 16.
Further, when you switch jobs in a year, then you should furnish your previous employer’s income and TDS details to your new employer in Form 12B.
You can read more here.
Q- I want to claim a deduction under Chapter VI-A / other exemptions/allowances in my income tax return which is not in my Form 16? Can I do it?
In a case where your employer issues you a Form 16 without any deductions, you can still claim the deduction while filing your income tax return. Form 16 is just a certificate issued by your employer that certifies the deduction of tax (TDS) on your salary. It’s just a base document for return filing, not the final return itself. You can always benefit from the deductions you are eligible for while filing your income tax return, even if the same is not mentioned in your Form 16.
Have trouble filing your income tax return? Just click here!
Q- Salary arrears received but not shown in From 16, what to do?
If you have received salary arrears, but the arrears are not shown in Form 16, then you can also show your arrears in the income tax return. All you require is all the details of salary in arrears and Form 10E, which is required to claim relief on salary arrears under section 89(1).
Q- Is Form 16 different from Form 60?
Form 60 is a declaration made by individuals who do not have a PAN, whereas Form 16 means an income certificate issued by the employer to an employee.
Q- Is Form 16 B is same as Part B of Form 16?
Form 16B is a certificate of tax deducted on the sale of the property. In contrast, Part B of Income Tax Form 16 consists of all the details of salary breakup, deduction, and taxes paid by an employer on behalf of employees.
Q- Will I get Form 16 from my employer even if there is no TDS?
Form 16 is a TDS certificate & it is issued only when there is tax deducted. Therefore, if there is no tax deducted, the employer is not required to issue Form 16 to you. The purpose of Form 16 is to serve as proof of tax deducted & deposited on your behalf. However, many employers, especially corporates, issue form 16 irrespective of the fact whether TDS has been deducted or not
Q- When Form 16 is required? What is the importance of Form 16?
Form 16 is required when you are filing your income tax return. This form serves as proof that your employer has deducted tax from your salary and deposited it with the Income Tax Department.
Q- What is the Form 16 issue date?
All employers, if they deduct TDS, are required to issue Form 16 by 15th June of the following year, immediately after the financial year in which the tax is deducted.
Q- I receive family pension income. Is it taxable as salary income & will I receive Form 16?
No, family pension is not taxable under the head “Income from Salary” because it comes within the ambit of “Income from Other Sources.” Therefore, Form 16 is not required to be issued in such cases.
Q- What is the difference between Form 16 & 16A?
Both Form 16 & 16A are TDS certificates. While Form 16 represents tax deducted for salaried employees, Form 16A represents tax deducted on income other than salary.
Q- What is Form 16 MCGM?
Form 16, issued by the Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai (MCGM) is known as Form 16 MCGM. To download Form 16 MCGM, all you need to do is:
- Visit MCGM site http://form16.mcgm.gov.in/
- Provide the employee code in the column
- Select F.Y. for which you need Form 16
- Download Form 16
Q- How can I get Form 16 of the last two years?
Form 16 is issued by the employer to the employee; therefore, an employee can get Form 16 from the employer for any year worked for them.
Q- How can I get a Form 16, as I am a pension holder?
Pension holders can get their Form 16 from the respective bank because they are responsible for deducting TDS from the pension amount.
Q- Do I get Form 16 even if I am not liable to pay a tax?
Yes, you will get Form-16 whether tax is deducted or not.
Q- I missed taking a copy of my Form 16 from my previous employer. Is it possible to recover the same from a tax website?
No, Form 16 can only be given by the employer.
 Fast & Accurate
Fast & Accurate








